
Lunar gravity anomaly from high-resolution
line-of-sight acceleration and topography data
Sugano, T. and K. Heki, Earth Planets and Space, 56, 81-86, 2004.
Sugano, T. and K. Heki, Geophys. Res. Lett., 31, L24703,
doi:10.1029/2004GL022059, 2004.
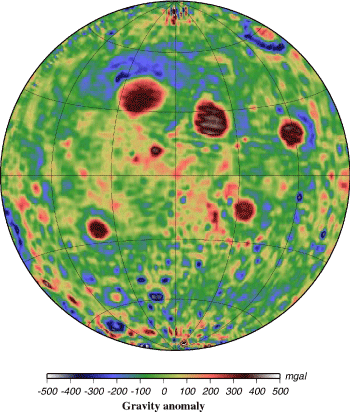
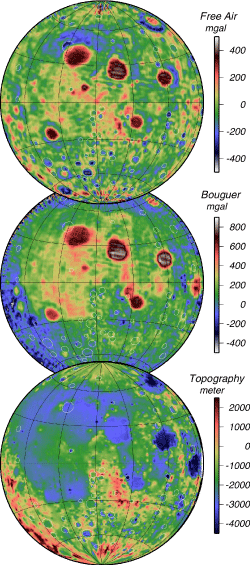
Line-of-sight acceleration data obtained by the Lunar Prospector (LP) extended low-altitude
mission were inverted to free-air gravity anomalies on the reference surface of the lunar
nearside. High-resolution topography data obtained by the Clementine laser altimetry were used
to convert the gravity anomalies to the Bouguer anomalies. Analysis of mass deficits of
medium-sized craters and mascon basins suggested that the lunar lithosphere was already
as thick as a few tens of kilometers when these features were formed.


